Positional number systems
In digital computers, data is generally represented as a sequence of binary digits, e.g. in the form of binary numbers. Since binary numbers are difficult to handle, we usually display them in the hexadecimal number system (i.e. in the positional number system with base 16) as hexadecimal numbers.
A number system (or number representation system) defines uniform rules which determine how we represent numbers by a series of digits.
- The base of a number system is a natural number that is greater than 1 (for example, 2, 10, or 16). Based on this, we speak, for example, of binary, decimal or hexadecimal number systems or notations.
- The idea of positional number systems is based on the concept of digits and their positional value.
For example,
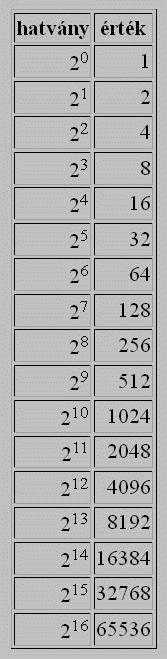
- in the binary number system, the set of digits is {0, 1}, and the positional values of digits are the powers of 2 whose exponents are natural numbers starting with 0;⇒
- the digits of the binary number system are called bits
- in the decimal number system, the set of digits is {0, 1, 2, ..., 9}, and the positional values of digits are the powers of 10 whose exponents are natural numbers starting with 0;
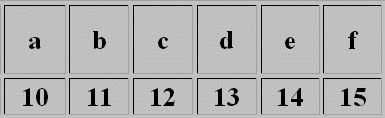
- in the hexadecimal number system, the set of digits is {0, 1, 2, ..., 9, A, B, ..., F}, and the positional values of digits are the powers of 16 whose exponents are natural numbers starting with 0.⇒ (Note that the digits A, B, ..., F correspond to the numbers 10, 11, ..., 15 in the decimal number system, respectively.⇒)
- In a positional number system, a given number is represented as a sequence of digits.
- In the case of non-integer (rational, real) numbers, a dot ('.') separates the integer and the fractional parts of the numbers.
- The value of a number is obtained by multiplying the value of each digit by its positional value and adding the resulting products. Performing the operations in the decimal number system, the final result of the addition will give the value of the number in decimal notation.
- For example, in the decimal number system, from right to left,
– the first positional value is 100=1 and so the corresponding digit represents the number of ones,
– the second positional value is 101=10 and so the corresponding digit represents the number of tens,
– the third positional value is 102=100 and so the corresponding digit represents the number of hundreds etc.In general, numbers in a number system with base 'b' can be described or represented by the following formula:

Examples:
(1) a real number in the decimal number system (b=10):
314.610 = 3*102+1*101+4*100 + 6*10−1(2) an integer in the binary number system (b=2):
1010112 = 1*25+1*23+1*21+1*20 = 4310(3) a real number in the binary number system (b=2):
101011.1012 = 1*25+1*23+1*21+1*20 + 1*2−1+1*2−3 = 43.62510(4) an integer in the hexadecimal number system (b=16):
1C416 = 1*162+12*161+4*160 = 45210(5) a real number in the hexadecimal number system (b=16):
1C4.416 = 1*162+12*161+4*160 + 4*16−1 = 452.2510